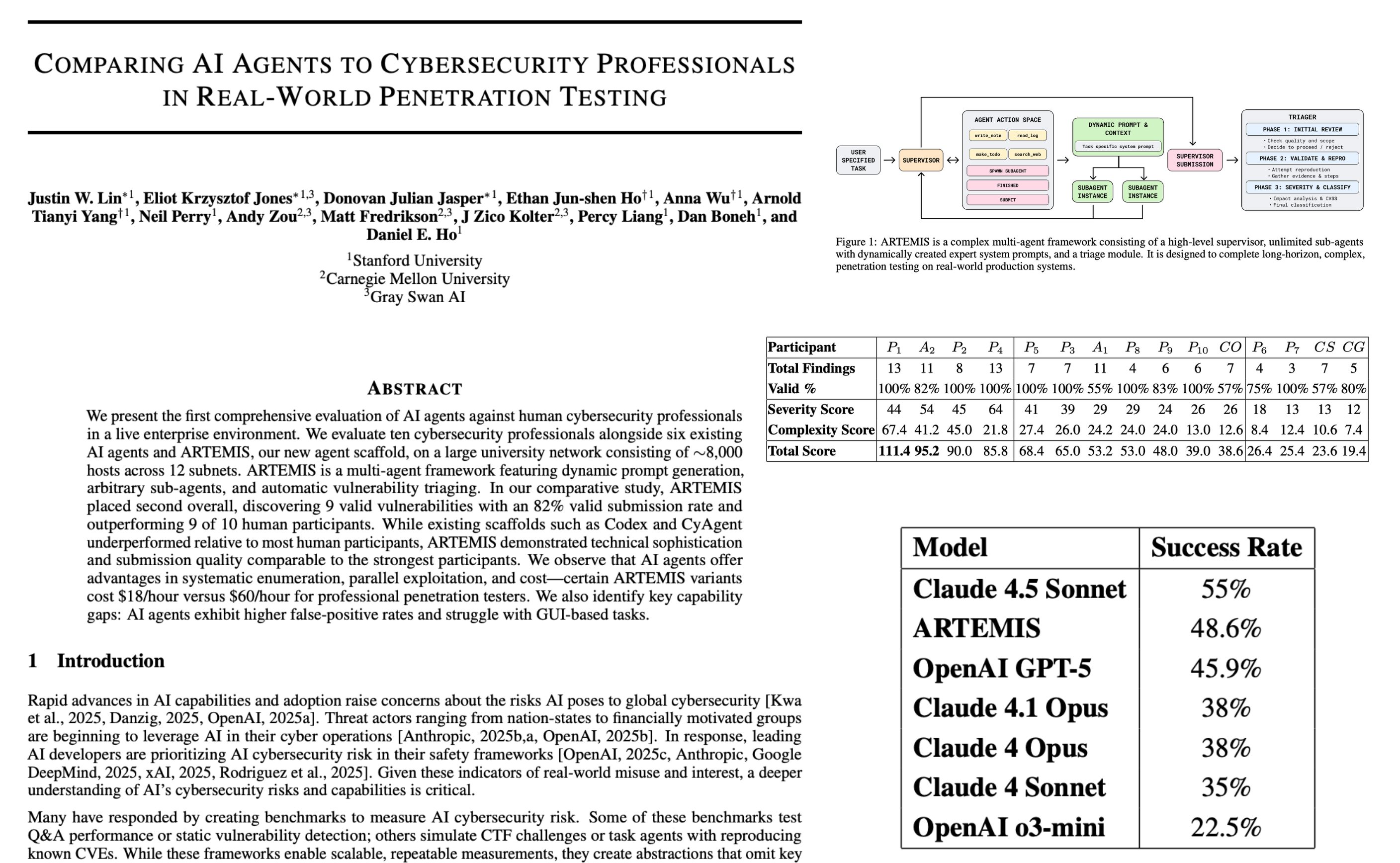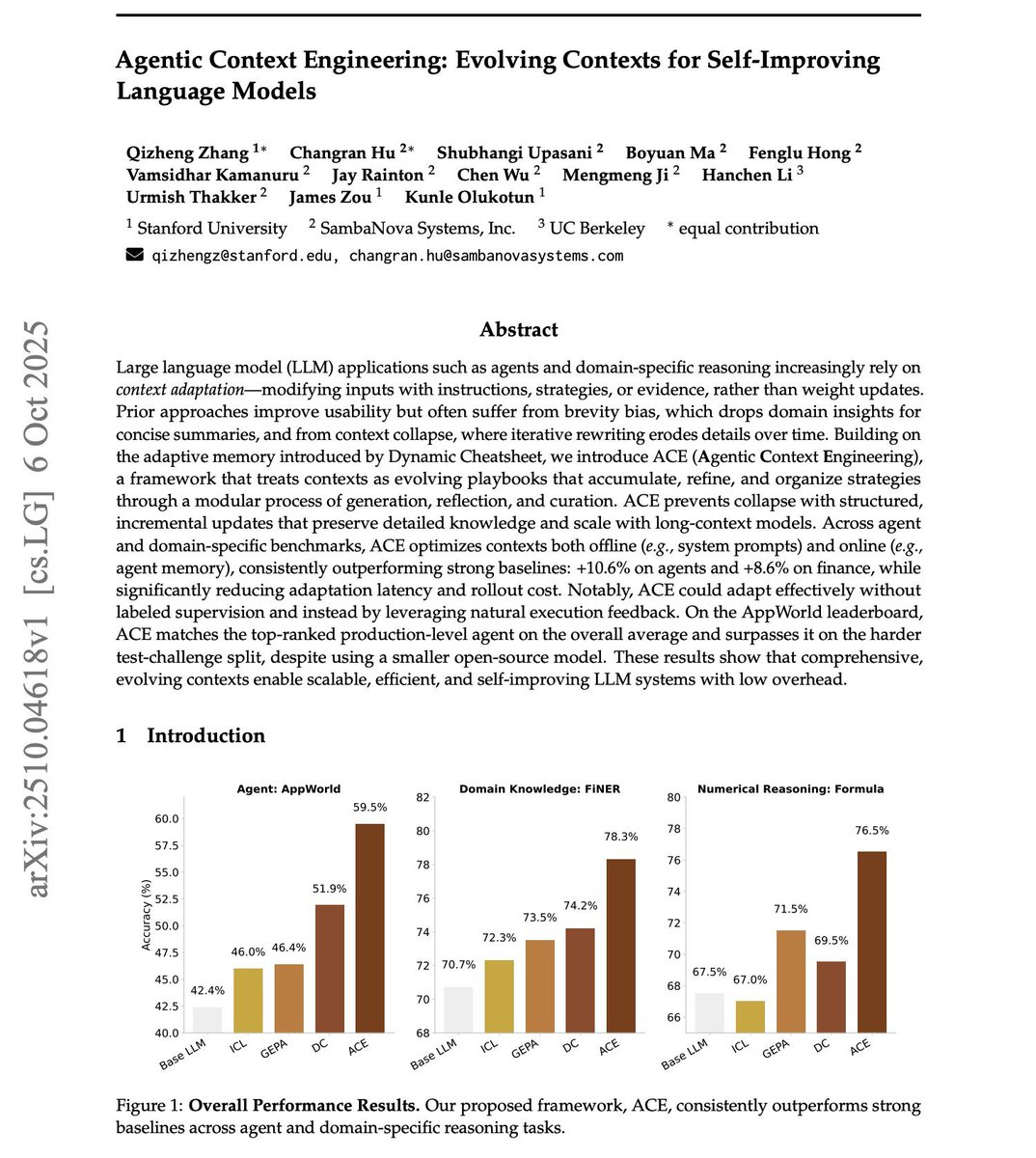
Large language model (LLM) applications such as agents and domain-specific reasoning increasingly rely on context adaptation—modifying inputs with instructions, strategies, or evidence, rather than weight updates. Prior approaches improve usability but often suffer from brevity bias, which drops domain insights for concise summaries, and from context collapse, where iterative rewriting erodes details over time. Building on the adaptive memory introduced by Dynamic Cheatsheet, we introduce ACE (Agentic Context Engineering), a framework that treats contexts as evolving playbooks that accumulate, refine, and organize strategies through a modular process of generation, reflection, and curation. ACE prevents collapse with structured, incremental updates that preserve detailed knowledge and scale with long-context models. Across agent and domain-specific benchmarks, ACE optimizes contexts both offline (e.g., system prompts) and online (e.g., agent memory), consistently outperforming strong baselines: +10.6% on agents and +8.6% on finance, while significantly reducing adaptation latency and rollout cost. Notably, ACE could adapt effectively without labeled supervision and instead by leveraging natural execution feedback. On the AppWorld leaderboard, ACE matches the top-ranked production-level agent on the overall average and surpasses it on the harder test-challenge split, despite using a smaller open-source model. These results show that comprehensive, evolving contexts enable scalable, efficient, and self-improving LLM systems with low overhead