 November 22, 2025
November 22, 2025
Short example of doing image segmentation with YOLOv11 (Ultralytics)
from ultralytics import YOLO
import random
import cv2
import numpy as np
model = YOLO("yolo11x-seg.pt")
img = cv2.imread("YourImagePath")
# if you want all classes
yolo_classes = list(model.names.values())
classes_ids = [yolo_classes.index(clas) for clas in yolo_classes]
conf = 0.2
results = model.predict(img, conf=conf)
colors = [random.choices(range(256), k=3) for _ in classes_ids]
for result in results:
for mask, box in zip(result.masks.xy, result.boxes):
points = np.int32([mask])
color_number = classes_ids.index(int(box.cls[0]))
cv2.fillPoly(img, points, colors[color_number])
cv2.imshow("Image", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.imwrite("YourSavePath", img)
Sumber:
 October 30, 2025
October 30, 2025
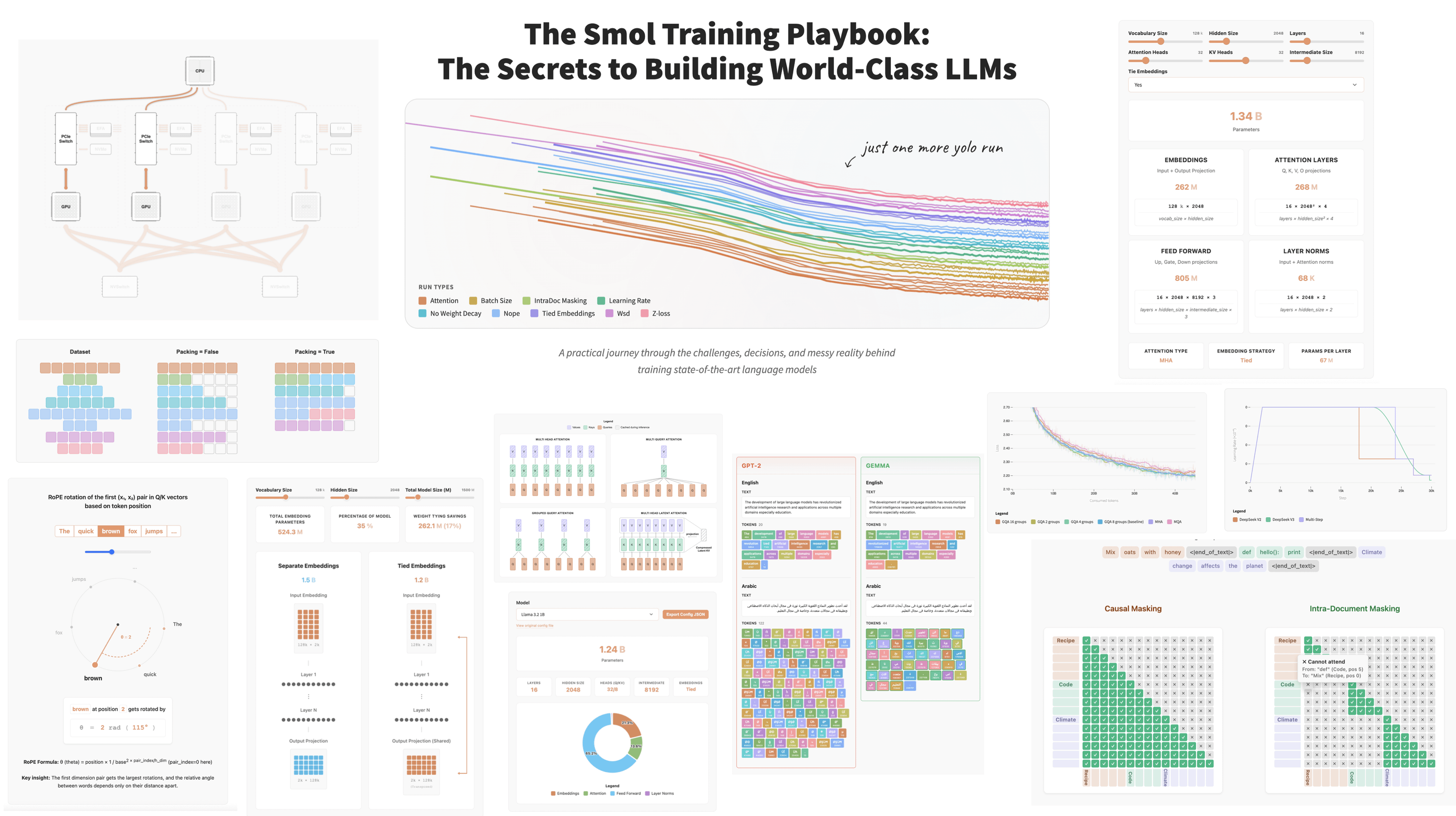
Sumber:
 September 16, 2025
September 16, 2025
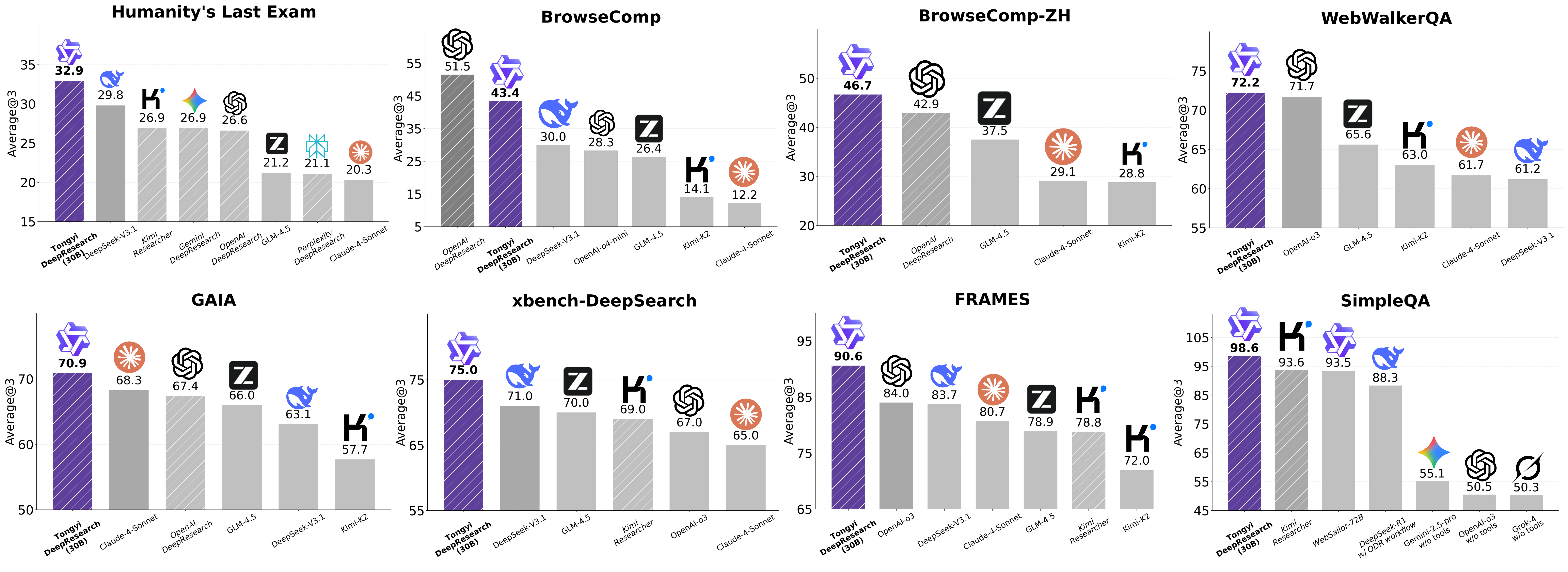
From Chatbot to Autonomous Agent
#
We are proud to present Tongyi DeepResearch, the first fully open-source Web Agent to achieve performance on par with OpenAI’s DeepResearch across a comprehensive suite of benchmarks. Tongyi DeepResearch demonstrates state-of-the-art results, scoring 32.9 on the academic reasoning task Humanity’s Last Exam (HLE), 43.4 on BrowseComp and 46.7 on BrowseComp-ZH in extremely complex information‑seeking tasks, and achieving a score of 75 on the user-centric xbench-DeepSearch benchmark, systematically outperforming all existing proprietary and open-source Deep Research agents.
 September 13, 2025
September 13, 2025
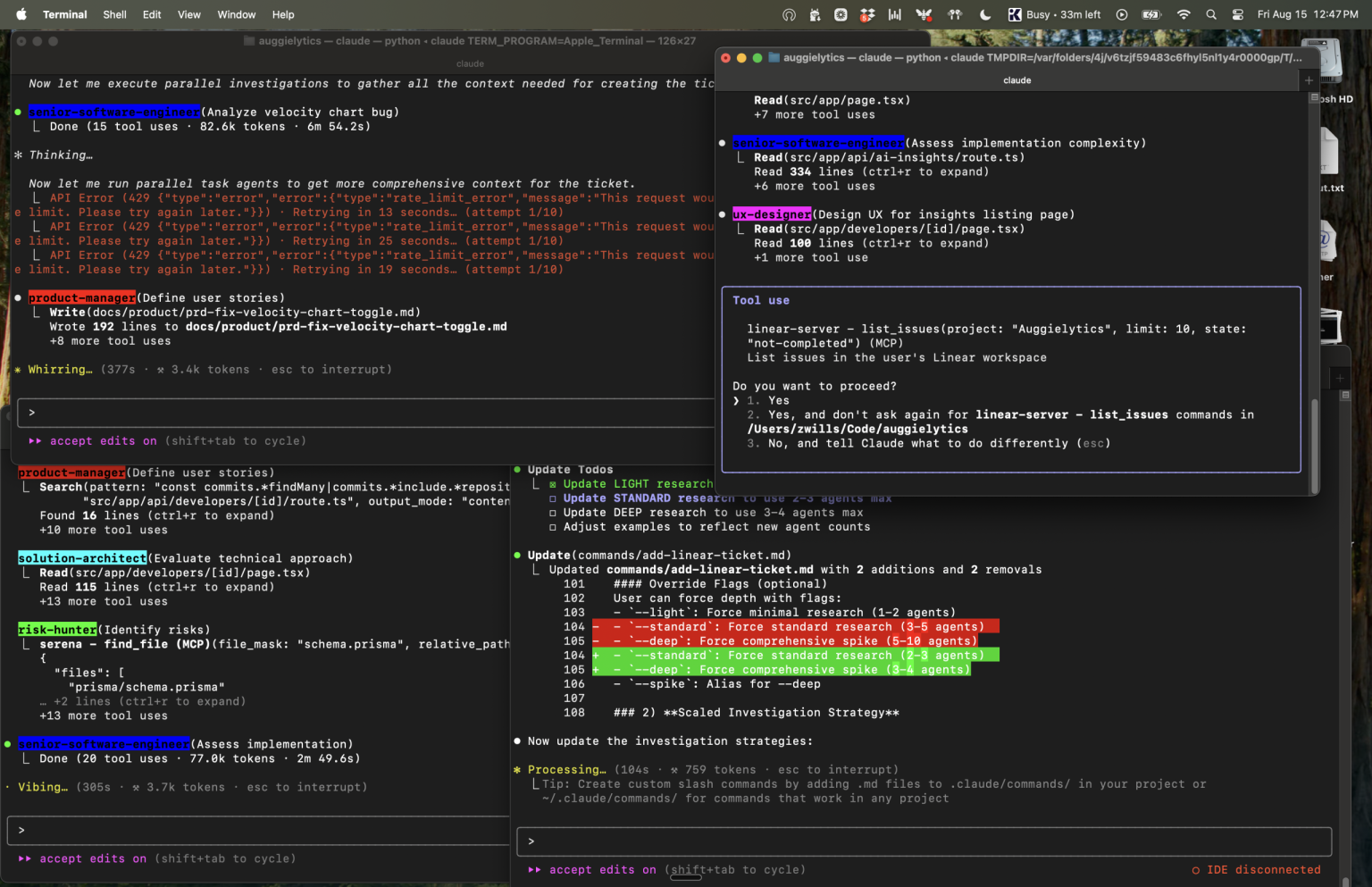
Source: https://zachwills.net/how-to-use-claude-code-subagents-to-parallelize-development/
 September 6, 2025
September 6, 2025
Problem:
#
create pair of of people with similar properties. Minimize difference between members of a pair
Solution
#
Algorithm for optimal node pairing that minimizes the total distance between paired nodes. This is essentially a minimum-weight perfect matching problem.I’ve created a comprehensive implementation of optimal node pairing algorithms. Here’s what the code includes:
Key Components:
#
- Node Class: Represents a point in 2D space with distance calculation
- Multiple Algorithm Approaches:
- Greedy: Fast O(n³) algorithm that repeatedly finds closest pairs
- Nearest Neighbor: O(n²) algorithm that pairs each node with its nearest unpaired neighbor
- Approximation with Local Search: Improves greedy solution using 2-opt style swaps
- Brute Force Optimal: Guaranteed optimal solution via backtracking (exponential time)
Algorithm Trade-offs:
#
- Greedy: Fast but may get stuck in local optima
- Nearest Neighbor: Faster, good for large datasets, decent quality
- Approximation: Best balance of speed and quality for medium datasets
- Brute Force: Perfect solution but only practical for small instances (≤8-10 nodes)
Usage Recommendations:
#
- Small datasets (≤8 nodes): Use brute force for guaranteed optimal
- Medium datasets (10-100 nodes): Use approximation algorithm
- Large datasets (>100 nodes): Use nearest neighbor or greedy
The code includes a test function that demonstrates all algorithms on a sample dataset, showing the total distance and individual pairs for each approach. You can easily adapt it for your specific coordinate system or distance metric.
 September 4, 2025
September 4, 2025
Mengukur detak jantung menggunakan WiFi. Pakai ESP32 dan Raspberry Pi juga bisa.
https://news.ucsc.edu/2025/09/pulse-fi-wifi-heart-rate/
papernya:
 August 28, 2025
August 28, 2025
Buku ini berisi referensi untuk kuliah pemrograman bahasa assembly untuk tingkat perguruan tinggi. Set instruksi yang dibahasa adalah x86-64 untuk prosesor x86-64 menggunakan sistem operasi Ubuntu 64 bit.
Kode di buku ini diuji di Ubuntu versi 22.04 LTS

Source:
 August 27, 2025
August 27, 2025
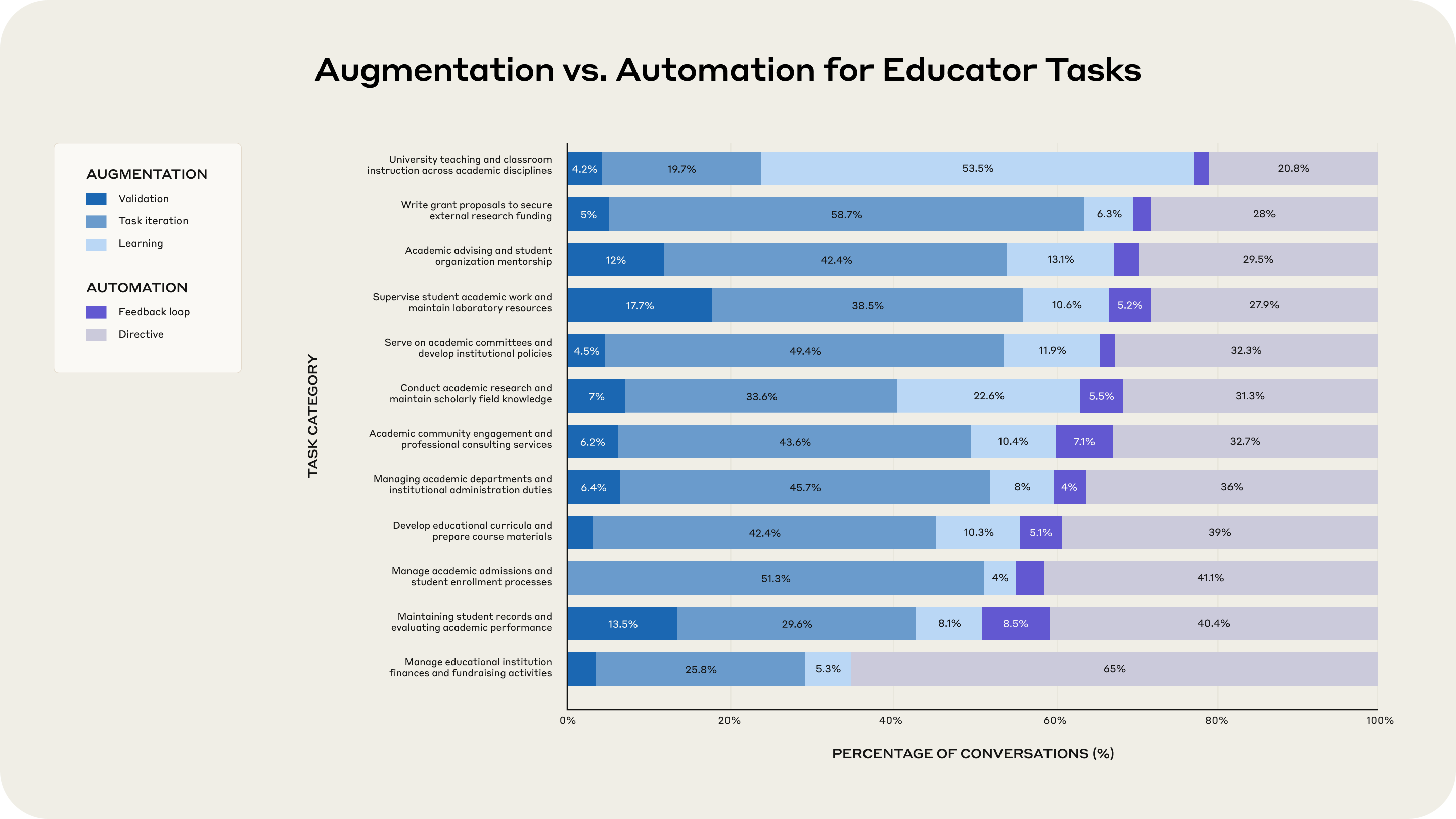
Today we’re releasing new @AnthropicAI research on how educators use AI, analyzing ~74,000 conversations from professors using @claudeai in collaboration with Northeastern University.
4 initial findings…
- Educators are builders, not just users of AI. Faculty are creating interactive chemistry simulations, grading rubrics, and data dashboards with Claude Artifacts.
- Educators automate the drudgery while staying in the loop for almost everything else. 77% of teaching and classroom instruction uses are collaborative, while 65% of financial/fundraising tasks are fully delegated. High-touch educational work remains human-centered.
- Notable tension in the data: 49% of grading conversations showed automation patterns, yet faculty rated this as AI’s least effective application. This disconnect highlights ongoing debates around appropriate AI use in assessment.
- AI is forcing pedagogical change. Professors are completely redesigning assessments—one shared: “I will never again assign a traditional research paper,” instead creating assignments requiring critical thinking even with AI assistance.
 August 27, 2025
August 27, 2025
Abstrak
Abstract: We present Jet-Nemotron, a new family of hybrid-architecture language models, which matches or exceeds the accuracy of leading full-attention models while significantly improving generation throughput. Jet-Nemotron is developed using Post Neural Architecture Search (PostNAS), a novel neural architecture exploration pipeline that enables efficient model design. Unlike prior approaches, PostNAS begins with a pre-trained full-attention model and freezes its MLP weights, allowing efficient exploration of attention block designs. The pipeline includes four key components: (1) learning optimal full-attention layer placement and elimination, (2) linear attention block selection, (3) designing new attention blocks, and (4) performing hardware-aware hyperparameter search. Our Jet-Nemotron-2B model achieves comparable or superior accuracy to Qwen3, Qwen2.5, Gemma3, and Llama3.2 across a comprehensive suite of benchmarks while delivering up to 53.6× generation throughput speedup and 6.1× prefilling speedup. It also achieves higher accuracy on MMLU and MMLU-Pro than recent advanced MoE full-attention models, such as DeepSeek-V3-Small and Moonlight, despite their larger scale with 15B total and 2.2B activated parameters.
 August 26, 2025
August 26, 2025
Fakta-fakta:
#
- Fact 1: Employment for young workers has declined in AI-exposed occupations
- Fact 2: Though overall employment continues to grow, employment growth for young workers in particular has been stagnant
- Fact 3: Entry-level employment has declined in applications of AI that automate work, with muted changes for augmentation
- Fact 4: Employment declines for young, AI-exposed workers remain after conditioning on firm-time shocks
- Fact 5: Labor market adjustments are visible in employment more than compensation
- Fact 6: Findings are largely consistent under alternative sample constructions






